Many modern electronics are powered by lithium-ion batteries.
As a result, lots of us have come across phones or laptops with dead or dying batteries. Considering electric vehicles use the same lithium-ion tech, should we be similarly worried that EV batteries will eventually fail and leave us with big repair bills?
Let's find out…
How long does an EV battery last?
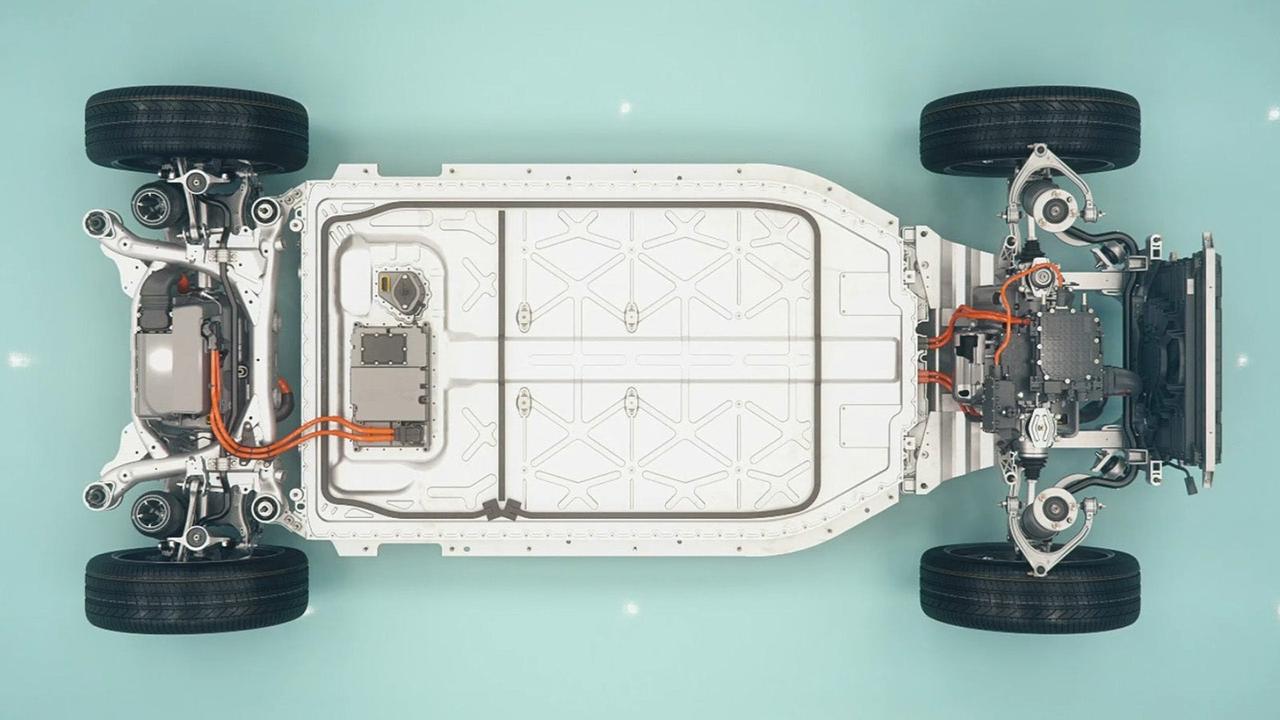
The first thing to understand is there are crucial differences that help an EV's lithium-ion battery pack last longer than the lithium-ion cells you'll find in your phone, for example:
- Lots of individual cells – phones usually use one singular battery cell, whereas an EV battery pack shares the load across dozens or hundreds of individual cells.
- Active temperature management – EVs pump liquid coolant around the pack to closely manage the temperature of individual cells, while phones and laptops usually rely on less-efficient air cooling.
- Battery management systems – EVs use computer-controlled battery management systems (BMS) that carefully balance the energy coming in and out of the pack so each individual cell shares the load equally.
- Larger safety margins – phones and laptops are often charged up to 100% before being heavily discharged, which puts a lot of stress on the cell. EV battery packs have built-in safety margins to stop them going all the way to 100% or 0%. Plus, EV owners can be extra careful by keeping their battery between 80% and 20% in normal use, and only charging all the way to 100% when tackling longer journeys.

So how long will an EV's pack last? Some valuable long-term data was provided in a recent Impact Report from Tesla. This shows that after 200,000 miles of driving, the packs in Model 3 and Model Y cars were retaining 85% of their original capacity on average, while larger Model S and Model X cars averaged 88% retention – very acceptable figures for such a long service life.
Another important factor is that most of the degradation happens in the first few years, with the car losing less and less capacity each year as it gets older, which is good news for long-term owners.
Assuming battery packs from other carmakers are as long-lived as Tesla cars, it's reasonable to assume that the battery packs in today's EVs will last the life of the car. And don't forget EV technology is improving all the time, so battery packs will only become more resistant to capacity loss in the future.
What is EV battery degradation?

Charging and discharging (driving) your EV is achieved by shuttling lithium ions from an electrode on one side of your battery to the other, and vice versa. As these ions move across your battery, they cause each electrode to physically swell up and then shrink back down again as they're inserted and removed from the electrode's chemical structure.
This swelling and shrinking action happens every time you charge up and drive your EV. Over time, this causes the physical structure of the electrodes in your battery to break down, developing microscopic cracks that make it harder for lithium ions to get in and out of the electrode, limiting the battery's total capacity.
As covered above, EV batteries have many protective systems to minimise the amount of degradation they suffer. However, knowing the factors that affect degradation can help you maximise the service life of your EV:
- Depth of discharge – charging all the way to 100% before discharging to near 0% puts the most strain on your battery pack. Ideally, you should try to keep your battery between 80% and 20% in normal usage, recharging regularly in small amounts, rather than big recharges less often. Aim to only use the battery's full charge when travelling on longer journeys.
- Charging speeds – most EV owners usually charge at home, either from a 7kW wallbox or a three-pin plug. These slower charging speeds place less strain on your battery pack compared with DC fast charging, which can be as fast as 350kW. Lots of fast charging is likely to cause more degradation, although the difference is fairly minimal on modern batteries, especially if you minimise your depth of discharge.
- Temperature – EV batteries have a happy operating temperature between 15ºC and 35ºC. Your EV will actively manage its own battery temperatures, either warming itself up in the cold or keeping cool in the heat, minimising the amount of degradation it suffers. If you're driving to a charger, some EVs allow you to 'precondition' the battery, so it's at the perfect temperature to charge quickly once you arrive.
- How hard you drive – if you're always driving like Max Verstappen with the throttle pinned wherever you go, you'll put more strain on your battery as you'll regularly be asking it for its maximum power output. Like a fuel-powered car, this will shorten your vehicle's service life.
Are electric car batteries recyclable?
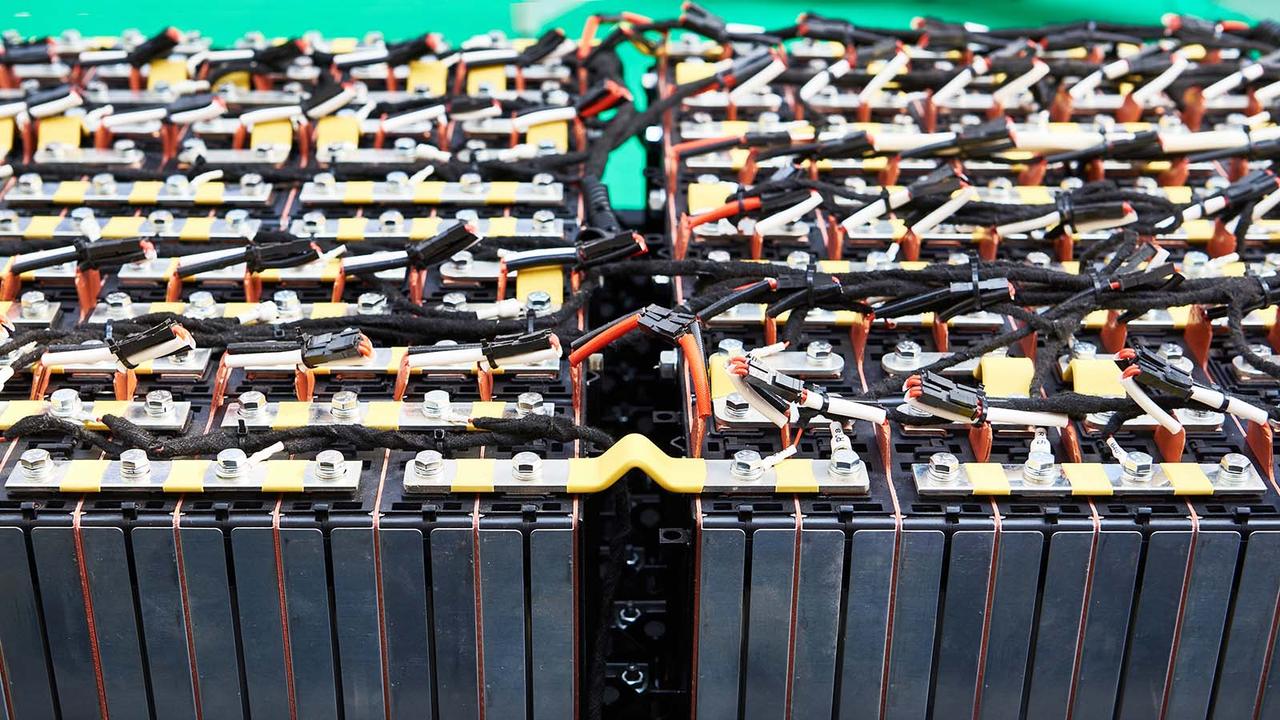
Yes, EV batteries are extremely recyclable. Reports suggest that, for every 100kWh of dead battery that gets recycled, you get 95kWh of fresh brand-new battery back, ready to be used in a new EV.
EV battery recycling makes a lot of economic sense, too. We'll probably see a point in the future where it's easier and cheaper to get fresh battery materials from recycled EV batteries, than digging up raw materials from the ground and processing them into new cells.
The recycling process itself is pretty interesting. Old packs are removed from cars and have their outer shells removed. From there, the entire module including the casing and all associated parts are thrown into an industrial crusher. The crusher spits out a mulched mix of metals and plastics from the casings, which are filtered off, and 'black mass' – a blend of all the active battery materials. This black mass is then chemically treated to separate the useful elements out, so they can be processed into new battery materials.
Can you repair EV batteries?
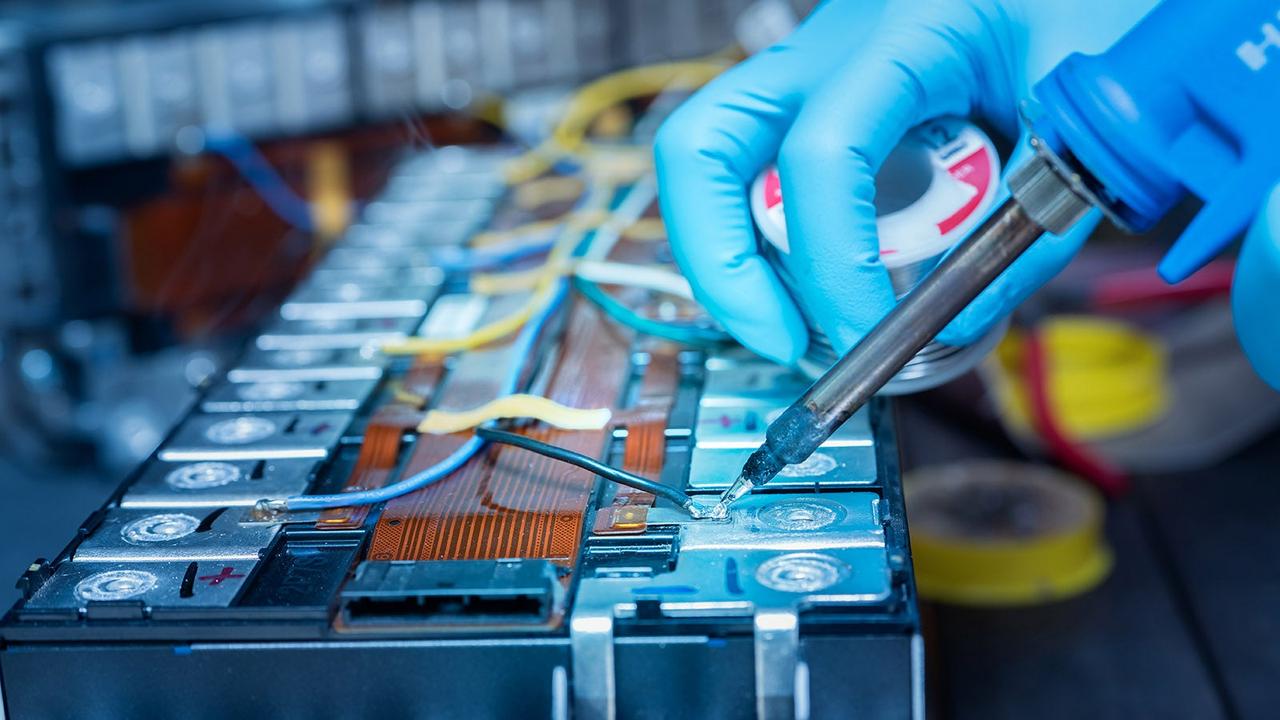
It is sometimes possible to repair a fault with an EV battery pack, but it's usually an expensive, complex and time-consuming job. At a certain point, it makes more financial sense to simply replace the battery pack with a new one, rather than go through the cost and difficulty of having the pack removed and disassembled so a repair can be performed.
EV brands may be unwilling to offer a repair to your battery if it needs one, as it's not cost-effective for them to devote shop time or space to a battery pack repair. As a result, you might need to enlist the services of a third-party EV specialist to see if a battery pack repair is a viable option for you.
How are EV batteries disposed of?

As covered above, EV batteries are relatively easy to recycle with a very high efficiency. As a result, there's no reason that an EV battery should ever be sent to landfill. Not only that, but several countries have already introduced legislation to forbid the disposal of EV batteries, which means many packs will sit in storage waiting to be recycled.
Sadly, it's likely that a decent proportion of dead EV batteries are still being sent for disposal, rather than being reclaimed for recycling. As global legislation becomes more stringent and the materials in dead EV batteries become more valuable, we hope the proportion being sent for recycling increases dramatically.
How much is an electric car battery?
This figure varies quite widely depending on your car's make and model, as well as the size of your battery. However, reports suggest it costs around £8,000 to have a replacement battery pack fitted to your EV, including parts and labour. For posh brands and bigger batteries, that figure could be comfortably over £10,000.
Bear in mind, however, that the battery packs in today's EVs should last the lifetime of the car if maintained properly. So, hopefully, most buyers won't have to budget for a replacement pack.
A 2024 study by US company Recurrent showed that, for EVs made from 2016 onwards, the average annual replacement rate was just 0.5%. That means the vast majority of those cars are still on the road and haven't required a replacement pack.
What are electric car batteries made of?

Ignoring all the supporting structure of steel, plastic, copper and aluminium that holds the pack together, the active parts of an EV's battery that actually store charge are usually made from a mix of lithium, nickel, manganese, cobalt and graphite. This is commonly referred to as NCM chemistry – nickel, cobalt and manganese – with those materials specifically forming the battery's cathode.
Some EVs use LFP chemistry. This is still a type of lithium-ion cell, but it relies on a cathode that contains lithium, iron and phosphorus. LFP batteries are a little less energy dense than NCM cells, but they're cheaper to produce and even more resistant to setting on fire if the battery is badly damaged in a crash.
Find a great-value electric car
Huge discounts are available on nearly new and used EVs available from Motorpoint. To see what options are available, check out our picks for the best electric cars on sale.



































